Image Thresholding Techniques with OpenCV
Learn how to apply basic and adaptive thresholding to images using OpenCV and Python, including practical examples and visualizations.
Overview
Thresholding is a fundamental technique in image processing that allows you to segment images by setting pixel values to either a maximum or minimum value based on a threshold. This is useful for separating objects from the background, document scanning, and more. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use both basic and adaptive thresholding methods in OpenCV with Python.
Prerequisites
You'll need the following Python libraries:
- opencv-python: For image processing operations
- matplotlib: For displaying images
- numpy: For numerical operations
Install them with:
pip install opencv-python matplotlib numpy
Step 1: Reading and Displaying the Image
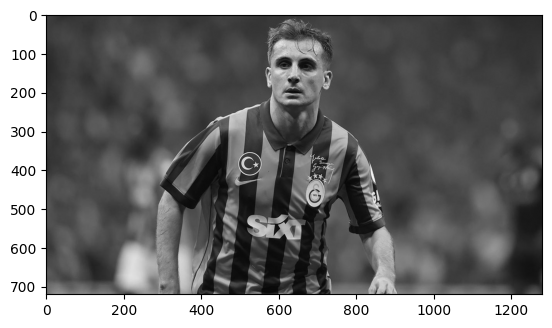
Let's start by reading an image and converting it to grayscale:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Read the image in grayscale mode
gray_img = cv2.imread('Assets/kerem.jpeg', 0)
plt.imshow(gray_img, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
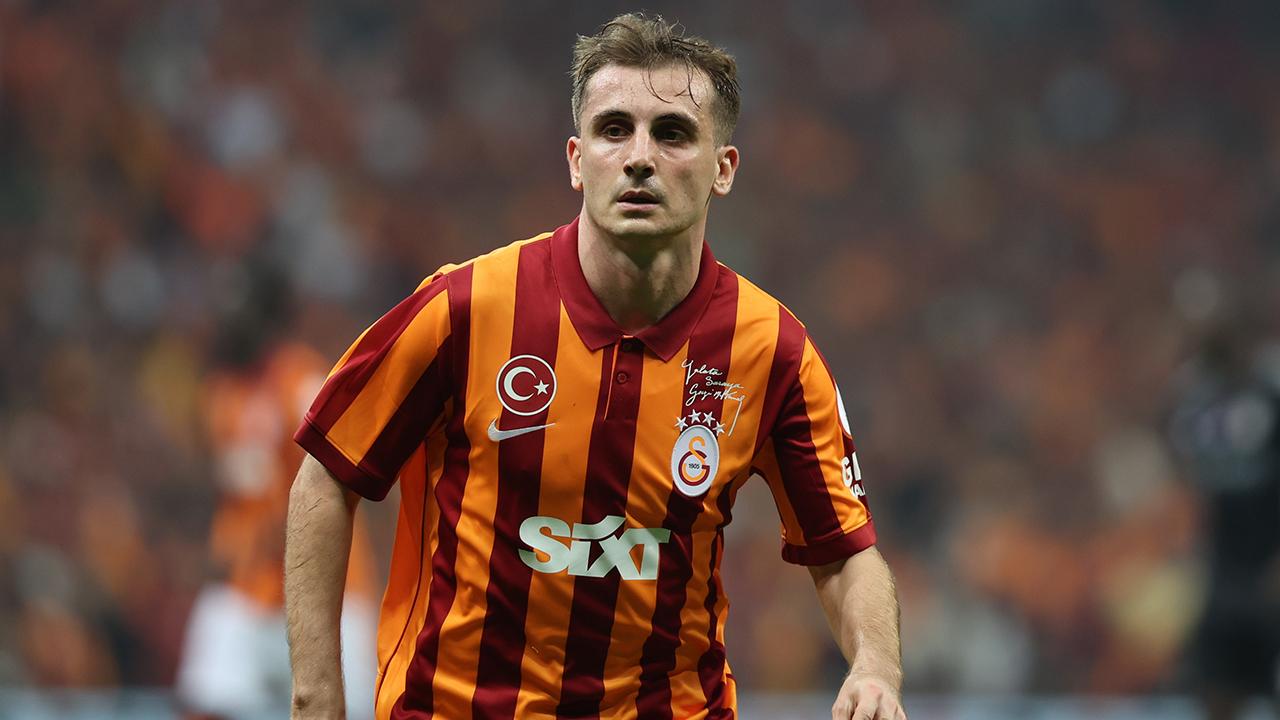

Step 2: Basic Thresholding
Thresholding assigns pixel values based on a threshold value. Any value below the threshold is set to 0, and values above the threshold are set to a maximum value.
# Apply a basic threshold
ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(gray_img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_TOZERO)
print(ret)
print(thresh1)
plt.imshow(thresh1, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
Common Thresholding Types in OpenCV
- THRESH_TRUNC: If pixel intensity is greater than the threshold, it is set to the threshlod value.
- THRESH_BINARY: If pixel intensity is greater than the threshold, it is set to 255, else set to 0.
- THRESH_TOZERO: Pixel intensity is set to 0 for all pixels less than the threshold value.
Step 3: Thresholding a Crossword Image
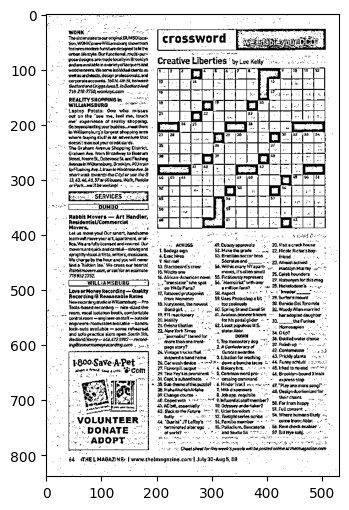
Let's try thresholding on a different image:
# Read a crossword image
gray_crossword = cv2.imread('Assets/crossword.jpg', 0)
def show(img):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
show(gray_crossword)


# Apply binary thresholding
ret, th1 = cv2.threshold(gray_crossword, 180, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
show(th1)

Step 4: Adaptive Thresholding
Adaptive thresholding calculates the threshold for a small region of the image, allowing for different threshold values in different areas. This is useful for images with varying lighting conditions.
# Adaptive thresholding
th2 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(
gray_crossword, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 8)
show(th2)
Parameters:
src: Source imagemaxValue: Maximum value to use with the THRESH_BINARY and THRESH_BINARY_INV thresholding typesadaptiveMethod: Adaptive thresholding algorithm to use (e.g.,ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_CorADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C)thresholdType: Type of thresholding (e.g.,THRESH_BINARYorTHRESH_BINARY_INV)blockSize: Size of a pixel neighborhood used to calculate the threshold value (must be odd)C: Constant subtracted from the mean or weighted mean
Note:
Adaptive Method Examples:
- cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C: The threshold value is the mean of the neighborhood area minus the constant
C. - cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C: The threshold value is a weighted sum (Gaussian window) of the neighborhood area minus
C.
Threshold Type:
- cv2.THRESH_BINARY: If the pixel value is greater than the threshold, it is set to the maximum value (e.g., 255); otherwise, it is set to 0.
- cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV: Inverse of THRESH_BINARY; pixels above the threshold are set to 0, and those below are set to the maximum value.
Step 5: Blending Thresholded Images
You can blend two thresholded images to combine their effects:
# Blend two images with different weights
blended = cv2.addWeighted(src1=th1, alpha=0.6, src2=th2, beta=0.4, gamma=0)
show(blended)
